Biochemistry – The Biochemistry Online – Free Online Lectures for Medical, Dental and Allied Health Sciences students by the Biochemistry Club.
Alpha Oxidation of Fatty acids
Alpha Oxidation
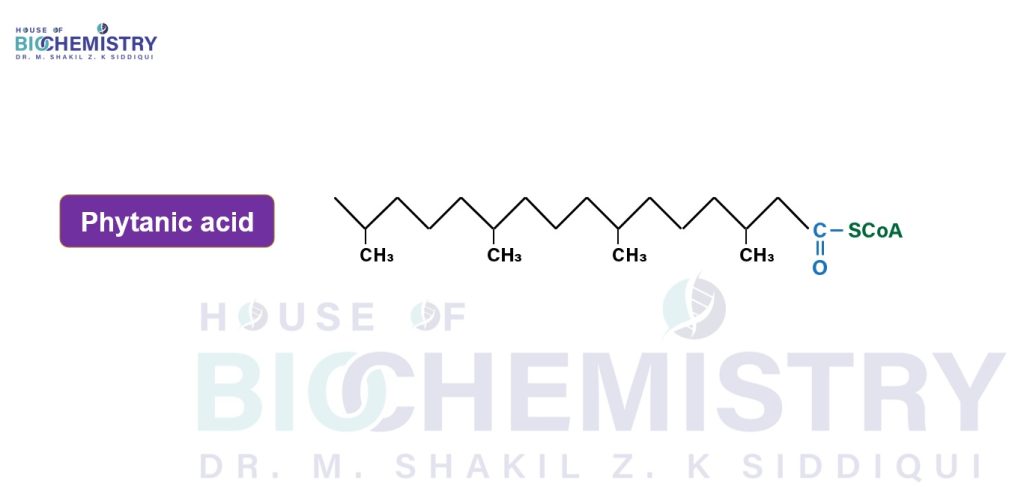
Phytanic acid is a branched chain Fatty acid with a methyl group at its β-Carbon.
Phytanic acid cannot be oxidized by acyl CoA dehydrogenase because of the methyl group on its β-carbon.
Instead, it is hydroxylated at the α-carbon by Phytanoyl CoA α-hydroxylase (PhyH).
The Carbon at the position no. 1 is released as CO2, and the product, 19-carbon pristanal, is oxidized to pristanic acid, which is then activated to its CoA derivative and then undergoes β-oxidation.
Refsum Disease
Refsum disease is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of peroxisomal Phytanoyl CoA α-hydroxylase (PhyH).
This results in the accumulation of phytanic acid in the plasma and tissues.
The symptoms are primarily neurologic, and the treatment involves dietary restriction to halt disease progression.
